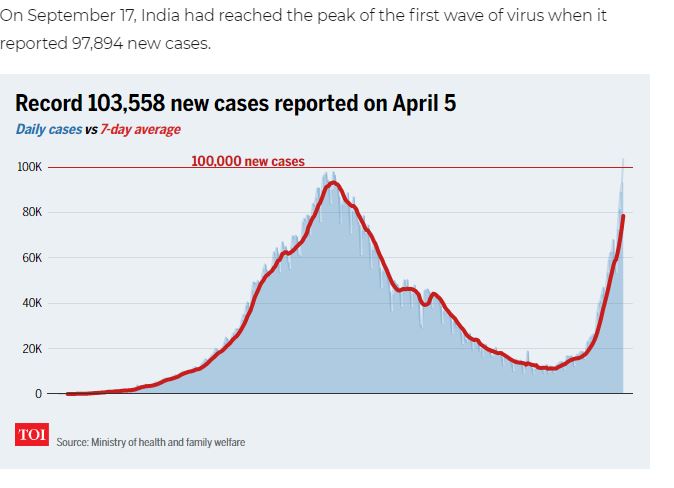
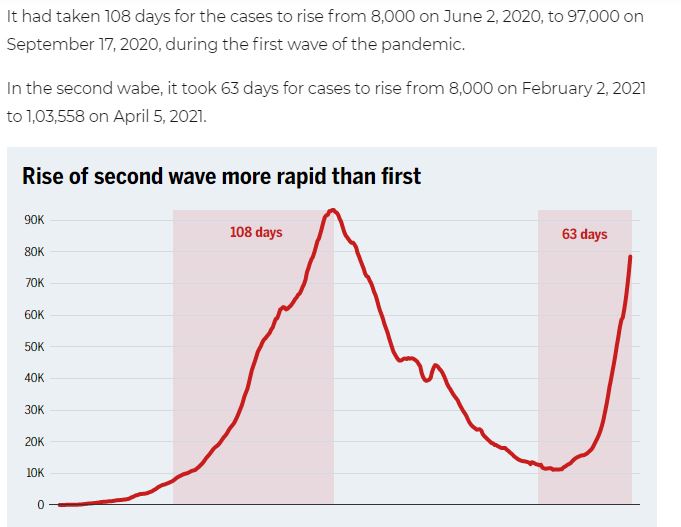
Introduction
Children are the future of the country and the upbringing of the children are of utmost importance for the development of the society.
Meaning: According to Convention on the Rights of Children,1989, the term ‘child’ means a human being below the age of 18 years,unless under the law applicable to the child,majority is attained earlier.
The African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the children,1990 defines a ‘child’ as a human being below the age of 18 years.
Children’s Rights History
In th 20th century, there were no standard for protection of children. They were to work alongside the adults. The situation compelled the international standards on child rights to evolve and it has advanced dramatically in the past century.
The League of Nations adopts the Geneva convention on December on the Rights of Children. The declaration articulates that all people owe to the children the right to development,special help in times of need,freedom and protection from exploitation and upbringing that instils social conscionsness and duty.
The U.N General Assembly establishes the International Children’s Emergency Fund with an emphasis on children throughout the world.
Convention on Rights of Children
According to Article 2, right to equality should be given to every child irrespective of any discrimination as to language,gender etc.
According to Article 3, the best interest of the child should be of primary consideration.Their protection and care is necessary in all aspects.
According to Article 5, the state shall respect the responsibilities,rights and duties of parents for the appropriate guidance of the children.
According to Article 6, every child has an inherent right to life.
According to Article 7, the child shall have the registered birth certificate immediately after birth.
According to Article 8, a child should not be seperated from their parents without his/her will unless it is necessary for the best interest of the child.
According to Article 11, the state should combat illicit transfer of child abroad.
Article 12 states that a child who is capable of expressing should have the freedom to express their views freely.
Article 18 states that the state shall take appropriate measures for the child-care services for working parents.
Article 23 says that a mentally retarded child should enjoy a full and decent life.
According to Article 24, health care and facilities for treatment of children is provided.
According to Article 26, every child shall have security and insurance benefits.
According to Article 27, a child should have a decent standard of living .
Article 28 states right to education to children.
There are as many as 54 articles of the convention which are widely accepted in the world including India. These articles are very crucial for the all round development of a child.
Indian Laws on human rights of Children
Fundamental Rights
According to Article 15 (3) of the Fundamental Rights no descrimination shall prevent the state from making any special provision for women and children.
Article 21A of the Fundamental Rights provides free and compulsary education to children of the age group of 6 to 14 years.
According to Article 23-24 of the Fundamental Rights the exploitation and trafficking of human beings and forced labours should be abolished and employment of children below 14 years in prohibited.
Directive Principles of State Policy
According to DPSP Article 39 (f) the children should be given an opportunity to develop in a healthy environment and youths are protected against moral and material abandonment.
According to Article 45 of DPSP free and compulsary education to children below 14 years were provided.
The 86th Amendment Act of DPSP,2002 made education a fundamental right under Article 21A. It also provided early childhood care and education for children until 6 years of age.
Juvenile Justice And Parole
The children who are found in conflict with the law are sent to juvenile homes instead of jails. Moreover some of them are also released on admonition that is after giving warning but their punishment should not be of life imprisonment or hanging.
Child labour Act, 1986
The act prohibits employment of children below 14 years of age in any sort of work.
The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POSCO) Act
The Act provides protection of children from offences of sexual assault, harrasment etc while safeguarding the child in every stage of judicial proceedings.
Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
It restricts the practice of child marriage that is below the age of 18 years for girls and 21 years for boys.
Conclusion
The rights of children should be protected and the government should take steps towards the welfare of the children. Though many rights are enacted for the protection of the children yet these are not working towards the total welfare of the children. Till date, a lot of children are forbidden to attend schools in rural areas and they are bound to work for their livelihood from a very tender age. Trafficking of human beings and forced labours are yet another crucial problems which is going on in the world. More strict provisions should be made for the rights of the children so that they can develop in a healthy environment.
References: https://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/crc.aspx
Majumder P.K,Criminal minor Acts (volume 2)